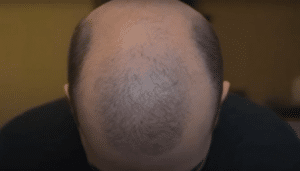
Balding genetics can be a confusing and difficult topic to understand. Genetics is a key factor in baldness, yet other elements like age, hormones, stress levels, and nutrition may also play a role.
In this blog post, we’ll examine the genetic basis of balding. We’ll discuss male pattern baldness (MPB) and female pattern baldness (FPB) as well as potential treatments for hair loss related to genetics such as FUE or FUT hair transplants. We’ll also look at different options available for treating genetic-related hair loss through FUE or FUT hair transplants.
So if you’re looking for answers on how to stop your own personal battle with balding genetics then read on.
Table of Contents:
- What is Genetic Balding?
- Hair Transplant Options for Treating Genetic Balding
- Male Pattern Baldness (MPB)
- Female Pattern Baldness (FPB)
- Conclusion
- FAQs in Relation to Balding Genetics
- Conclusion
What is Genetic Balding?

Genetic balding is a type of hair loss caused by genetic factors. Both sexes may be affected by this hereditary hair loss, yet it is more prevalent in males. Although the exact cause of genetic balding is still unknown, it is believed that certain individuals may be genetically predisposed to a higher risk of hair loss.
Causes of Genetic Balding:
Genetics plays an important role in determining the rate at which someone’s hair will thin or fall out over time. A person’s genes determine how sensitive they are to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that plays a major role in male pattern baldness (MPB). Higher DHT levels can lead to more hair loss than lower ones. Other possible causes include age, stress, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, medications, and certain medical conditions such as alopecia areata or thyroid disease.
Types of Genetic Balding:
There are two main types of genetic balding i.e. male pattern baldness (MPB) and female pattern baldness (FPB). MPB typically affects the top and front areas of the scalp while FPB tends to affect the sides and back areas more severely. Both types involve progressive thinning or shedding that can lead to complete hair loss if left untreated for too long.
While anyone can experience genetic balding regardless of gender or ethnicity, it is most commonly seen among Caucasian males aged 20-50 years old who have a family history of MPB or FPB. Furthermore, those with long-term ailments like diabetes may be more likely to experience genetic balding due to their weakened immunity and other health issues linked to these diseases.
Genetic balding, a type of hair loss often seen in aging individuals, is attributed to various causes including heredity. Hair transplants are an effective option for treating genetic balding and provide permanent results with minimal downtime.
Hair Transplant Options for Treating Genetic Balding
FUE Hair Transplants surgery involve harvesting individual follicles from areas of dense hair growth, which are then inserted into balding or thinning regions for a more natural-looking outcome with minimal scarring. The extracted follicles are then implanted into areas of baldness or thinning. This type of transplant can provide natural-looking results with minimal scarring, making it an attractive option for those who want to restore their appearance without surgery.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) is a conventional hair restoration technique that involves removing a portion of skin from the donor region at the back or side of the scalp and utilising it to gather multiple hairs in one go. These hairs are then carefully placed into small incisions made in areas affected by genetic balding. While this method requires more downtime than FUE, it often yields better results due to its ability to transplant larger grafts at once.
Here’s a table comparing the key features of FUE and FUT for treating genetic balding:
| Feature | FUE Hair Transplant | FUT (Follicular Unit Transplant) |
| Harvesting Method | Individual follicles extracted | Strip of skin containing multiple follicles removed |
| Scarring | Minimal scarring at extraction sites | Linear scar at donor site |
| Recovery Time | Generally quicker recovery | Requires more downtime |
| Graft Transplant Capacity | Suitable for smaller graft counts | Can transplant larger numbers of grafts at once |
| Results | Natural-looking results | Often yields better results due to larger grafts |
Male Pattern Baldness (MPB)

Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) is a common form of hair loss that affects many men. It is caused by genetics and typically begins with thinning at the crown or temples, followed by a receding hairline. It can sometimes progress to complete baldness on the top of the head. MPB is often called “male-pattern baldness” because it follows a patterned progression in most cases.
Symptoms of MPB:
- Hair thinning or receding at the temples and crown.
- A pattern in an M-shape across the forehead and sides of the head.
- Baldness on top may be a sign of male pattern baldness.
- Some people may also experience itching or flaking scalp due to increased sensitivity from exposed skin cells.
Treatment Options:
- Mild MPB: Minoxidil may promote regrowth and delay further hair loss, but results are not guaranteed.
Severe MPB: Surgical procedures like FUE (follicular unit extraction) or FUT (follicular unit transplantation) may be recommended for permanent results.
Female Pattern Baldness (FPB)

Female Pattern Baldness (FPB) is a common form of hair loss that primarily affects females, often starting in the late twenties or early thirties, though it can occur earlier. It’s frequently hereditary and can manifest in various ways on the scalp.
Symptoms of FPB
- Thinning hair on the scalp’s crown, top, sides, and rear.
- Receding hairline along the sides or back.
- Widening part lines.
- Complete baldness in severe cases.
- Excessive shedding during brushing, washing, or styling.
- Changes in hair texture from thick to fine or brittle.
- Increased visibility of the scalp due to reduced hair coverage.
Treatment Options
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Medication that stimulates new hair growth and slows further loss.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Relocates healthy donor follicles to areas with significant hair loss, offering a permanent solution if performed correctly.
- Scalp Micro-Pigmentation (SMP): Involves creating tiny dots on the scalp for a fuller appearance without incisions.
Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) vs. Female Pattern Baldness (FPB)
Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) is a genetic condition that affects many men and can be treated with various medical solutions. Let’s examine Female Pattern Baldness (FPB), a hair loss condition that predominantly impacts females.
Here’s a table comparing Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) and Female Pattern Baldness (FPB):
| Characteristic | Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) | Female Pattern Baldness (FPB) |
| Affected Gender | Mainly affects men | Predominantly impacts females |
| Pattern | Thinning at the crown, receding hairline, bald on top | Generalized thinning on top, widening part |
| Hormonal Influence | Influenced by androgens (male hormones) | Influenced by androgens and genetics |
| Treatment Approach | Minoxidil, finasteride, surgical options | Minoxidil, low-level laser therapy, PRP injections |
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points:
Genetic balding is a condition that affects many men and women. Genetic makeup, advancing years, hormonal fluctuations, and additional elements may all be contributory factors to this commonly experienced hair loss condition. There are two main types of genetic balding i.e. Male pattern baldness (MPB) and female pattern baldness (FPB). Treatment options for both MPB and FPB include medications, hair transplants, lifestyle changes such as diet or exercise modifications, scalp massage therapy, laser therapy, platelet-rich plasma injections (PRP), etc. Hair transplants can be done through either FUE or FUT techniques with varying success rates depending on the individual’s case.
FAQs in Relation to Balding Genetics
Is balding 100% genetic?
No, balding is not 100% genetic. Although genetics may be a factor in hair loss, other conditions such as stress and hormonal imbalances can also have an impact. Additionally, certain lifestyle choices like smoking or poor nutrition may lead to thinning of the hair. Therefore, it is essential for individuals who are having hair loss to examine all potential causes prior to searching out treatment plans.
Is there a genetic basis for hair loss?
Yes, there exists a hereditary factor that can contribute to hair loss. Studies have shown that male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness are both caused by an inherited gene from either parent. High levels of DHT, a hormone that can lead to follicle miniaturization and thinning or balding of the scalp, are caused by an inherited gene from either parent. Additionally, some medical conditions such as alopecia areata and thyroid disease may also cause hair loss due to their effects on hormones.
Is hair loss inherited from the mother or father?
Hair thinning may not be necessarily inherited from either parent, though it can potentially be passed on genetically. It’s important to note that hair loss does have a genetic component and certain conditions such as male pattern baldness may be more likely to occur if you have family members who are affected by it. Stress, hormones, diet, and lifestyle may all be contributory elements to hair loss. Nevertheless, it is not feasible to definitely assert that the condition has been passed down from either parent. Therefore, it is not possible to definitively say that hair loss is inherited from either the mother or father.
Does the balding gene come from Dad?
No clear-cut answer exists to this query, as there is a multitude of elements that can lead to hair loss. While genetic predisposition to androgenic alopecia may be inherited from one’s father. Other factors such as medical conditions, hormonal imbalances, stress, or lifestyle choices can also cause hair loss. Therefore, it cannot be said with certainty whether or not the balding gene comes from one’s father.
Are You Ready to Fight Your Balding Genetics Once and For All?
In conclusion, balding genetics is a complex issue that affects both men and women. Hair transplants are one of the most effective solutions for treating genetic balding, with FUE and FUT being two popular options. Male pattern baldness (MPB) typically begins at the temples or crown area while female pattern baldness (FPB) usually starts around the part line in thinning hair.
Understanding your own personal genetic makeup can help you determine which treatment option may be best suited to address your individual needs when it comes to addressing hereditary hair loss caused by genetics.
Take control of your balding genetics and regain confidence with the best hair transplant procedures available. Schedule a consultation today to learn more about how you can benefit from our advanced restoration techniques.
Best Hair Transplant
1970 S. Prospect Ave., Suite 2
Redondo Beach, CA 90277
(213) 403-0455
https://www.google.com/maps?cid=9280610872186794918
To ensure your ease of mind, you can view our customer recommendations HERE. Furthermore, you can also see our Google reviews and Yelp reviews. We can’t wait to help you start restoring your lost hair.