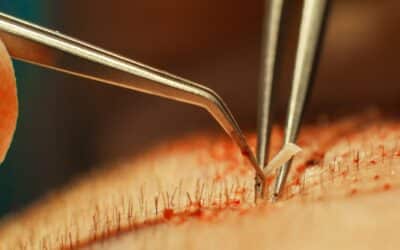
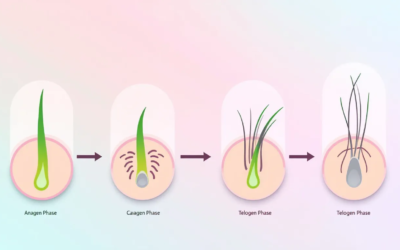
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a sought-after hair transplant method. However, like all procedures, there are instances where an FUE Hair Transplant can fail. Understanding these scenarios can equip individuals with the knowledge to get the best results.
How Does FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) Work?
FUE is a meticulous process wherein hair follicles are extracted from a donor area, typically the back of the head, and then implanted into the recipient area. The procedure is conducted under local anesthesia and can span several hours. The main appeal lies in its ability to give natural-looking results without significant incisions.
- Donor Area: This region is often resistant to balding, ensuring the longevity of transplanted hairs.
- Grafting: Once extracted, the follicles are prepared for transplantation.
- Natural Look: Skillful implantation ensures hairs grow in their natural direction.
- Duration: Depending on the area size, the procedure can last from 4 to 8 hours.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia ensures the patient remains comfortable throughout.
- Technological Advancements: New tools have made the process even more refined.
Table of Contents:
- What is FUE Hair Transplant?
- Reasons Why FUE Hair Transplants Can Fail
- How to Avoid Failure with FUE Hair Transplants?
- Aftercare Tips for Successful FUE Hair Transplants
- Alternatives to FUE Hair Transplants
- FAQs in Relation to Can Fue Hair Transplant Fail?
- Conclusion
Leading Causes for FUE Hair Transplant Failure

Following are some factors in which FUE hair transplant can fail:
Poor quality grafts
For the hair transplant to be effective, the donor area has to have strong, healthy hair grafts. Poor-quality grafts might not take root or might only sprout a few hairs. The patient’s age, the condition of the hair follicles, and the quantity of sun exposure the donor area has gotten are some of the variables that affect the quality of the grafts.
Inexperienced surgeon
A hair transplant is a delicate procedure that requires a skilled surgeon. If the surgeon is inexperienced or needs to be adequately trained, they may make mistakes that can lead to the failure of the hair transplant. This includes making too deep or shallow incisions, damaging the grafts, or not placing the grafts in the correct location.
Infection
Any surgery carries the risk of infection, and a hair transplant is no exception. If the incisions are not properly cleaned and cared for, an infection can develop, damaging the grafts and leading to their failure. The patient should be careful to follow the surgeon’s instructions for aftercare, which will typically include washing the scalp with soap and water and applying an antibiotic ointment to the incisions.
Allergic reaction
The local anaesthetic or other drugs used during the hair transplant might cause an adverse reaction in the patient. This might harm the grafts by causing swelling, redness, and itching. Before the operation, the patient should disclose to the surgeon any allergies they may have.
Scarring
The FUE hair transplant procedure involves making small incisions in the scalp to extract the grafts. These incisions can leave scars, which can be unsightly and may affect the natural appearance of the hair. The size of the scars will depend on the technique used by the surgeon and the patient’s healing response.
Unrealistic expectations
Patients with unrealistic expectations about what a hair transplant can achieve are more likely to be disappointed with the results. It is essential to be realistic about what the procedure can do and to set realistic expectations before undergoing a hair transplant. A good surgeon can discuss the patient’s expectations and help them develop a realistic plan for their hair transplant.
Inadequate aftercare
The patient must follow the surgeon’s instructions carefully for aftercare to ensure the success of the hair transplant. Failure to follow the aftercare instructions can increase the risk of infection, scarring, and other complications. The patient should wash their scalp regularly, apply antibiotic ointment to the incisions, and avoid strenuous activity for a few days after the procedure.
Genetic factors
In some cases, hair loss is caused by genetic factors beyond the patient’s or surgeon’s control. Even with a successful hair transplant, these patients may continue to lose hair in other areas of the scalp. If the patient has a family history of hair loss, they should discuss this with the surgeon before undergoing a hair transplant.
Medical conditions
Some medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and certain medications, can increase the risk of hair loss. Patients with these conditions should talk to their doctor before undergoing a hair transplant. The doctor can help determine if the patient is a good candidate for hair transplant surgery and recommend a qualified surgeon.
Smoking
Smoking can impair blood circulation, which can affect the healing of the grafts and increase the risk of complications. Patients who smoke should quit smoking before and after a hair transplant. Smoking cessation can improve the chances of a successful hair transplant.
Age of the patient
Hair loss is more common in older men, and the success rate of hair transplants tends to be lower in older patients. This is because the hair follicles in the donor area may not be as healthy in older patients. The hair follicles in the donor area become less active as people age, and they may not be able to produce as many healthy hairs. Additionally, the scalp may be thinner in older patients, making it more difficult to transplant hair.
Severity of the hair loss
The more severe the hair loss, the less likely it is that a hair transplant will be successful. This is because there may not be enough donor hair to cover the bald areas. If the patient has lost a lot of hair, they may need multiple hair transplants to achieve their desired results.
Type of hair transplant technique used
There are two main types of hair transplant techniques: follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE). FUT is a more traditional technique that involves making a single incision in the scalp and removing a strip of tissue containing hair follicles.
The tissue is then divided into smaller grafts and transplanted into the balding areas. FUE is a newer technique that involves extracting hair follicles from the donor area using a small needle or punch. The grafts are then transplanted into the balding areas.
FUE is generally considered more precise than FUT and has a lower risk of scarring. However, it is also more expensive than FUT. The best type of hair transplant technique for a particular patient will depend on the patient’s individual needs and preferences.
Patient’s overall health
Patients in good overall health are more likely to have a successful hair transplant. This is because their bodies will be better able to heal from the surgery and support the growth of the transplanted hair. Patients with certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or diabetes, may have an increased risk of complications from hair transplant surgery. Discussing the patient’s medical conditions with the surgeon before undergoing a hair transplant is essential.
Signs and Symptoms of Unsuccessful Transplants
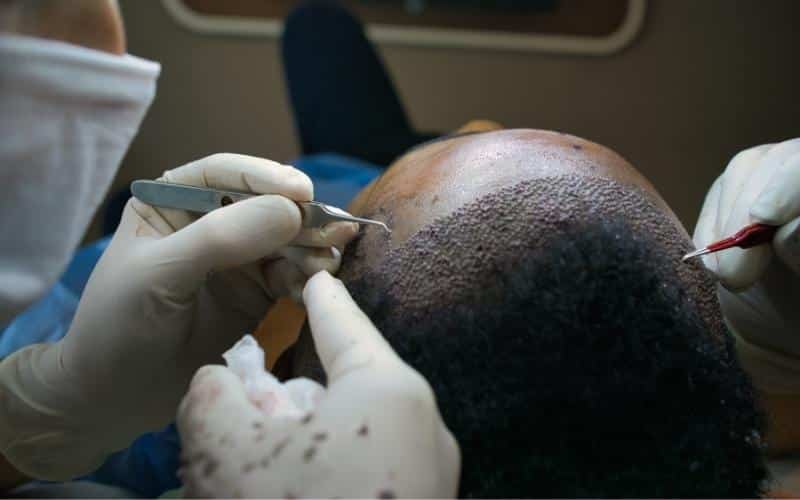
Not all unsuccessful FUE procedures are immediately apparent. Sometimes, the initial results seem promising, but issues arise weeks or months later. Common indicators include unnatural hair growth patterns, excessive shedding, and visible scarring.
| Sign/Symptom | Possible Cause | Remedial Action |
| Uneven Growth | Poor graft placement or angle | Corrective transplantation |
| Excessive Shedding | Poor graft survival | Re-evaluation & potential re-do |
| Redness & Inflammation | Infection or reaction | Medical intervention |
| Scarring | Poor technique | Scar treatment or camouflage |
| Lack of Density | Insufficient graft survival | Additional transplant sessions |
| Prolonged Pain | Underlying complications | Medical assessment & treatment |
Factors That Influence FUE Transplant Success Rate
The success of an FUE transplant isn’t solely dependent on the surgeon’s skill. Patient characteristics, like the quality of donor hair, age, and general health, play crucial roles. Ensuring a comprehensive consultation can set realistic expectations and improve outcomes.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Success |
| Donor Hair Quality | Health & strength of donor’s hair | Directly proportional |
| Age Factor | Younger vs. Older scalp | Variable; different age groups have distinct challenges |
| Health & Lifestyle | Overall patient health and habits | Adverse habits can reduce the success rate |
| Scalp Elasticity | Flexibility of the scalp | Directly proportional |
| Post-Op Adherence | Following aftercare guidelines | Directly proportional |
| Expertise | Experience & skill of the surgical team | Directly proportional |
Post-Transplant Care: Key to Ensuring Success

After surgery, the patient is mostly responsible for ensuring the transplant succeeds. Important actions include adhering to the surgeon’s post-operative instructions, keeping the area clean, and being careful with the new grafts. The results of the transplant may suffer if these are neglected.
- Medications: Some may be prescribed to aid healing and prevent infections.
- Hair Washing Routine: Gentle washing techniques help protect the new grafts.
- Physical Activity: Restricting strenuous activities can aid recovery.
- Sun Exposure: Limiting direct sun can prevent damage and discoloration.
- Diet & Nutrition: A balanced diet can support optimal hair growth.
- Avoiding Harmful Habits: Refraining from smoking or alcohol can promote better healing.
Addressing Failed Transplants: What Are Your Options?

Corrective measures are available in the unfortunate event of a failed FUE procedure. Solutions range from medical interventions to additional transplant sessions. It’s crucial to consult with experienced professionals to determine the best course of action.
| Option | Description |
| Another hair transplant | This is the most common option for addressing a failed hair transplant. The surgeon will typically use the same technique as the first transplant but may also use a different technique if they believe it will be more successful. |
| Follicular unit extraction (FUE) | FUE is a newer hair transplant technique that is generally considered more precise and has a lower risk of scarring than the traditional FUT technique. This may be a good option for patients with a failed FUT transplant. |
| Hair restoration medication | Some hair restoration medications can help to stimulate hair growth in balding areas. These medications can be used with a hair transplant or as a standalone treatment. |
| Hairpieces | Hairpieces can be a good option for patients who have had a failed hair transplant and do not want to undergo another surgery. Hairpieces are available in various styles and colors and can be custom-made to fit the patient’s head. |
| Scalp micropigmentation (SMP) | SMP is a cosmetic procedure that can create the illusion of hair growth in balding areas. SMP involves tattooing tiny dots of pigment into the scalp to create the appearance of hair follicles. |
The journey to restoring hair is deeply personal. While FUE offers promising results, being well-informed about the potential for an FUE Hair Transplant to fail and how to navigate such situations can make all the difference. Collaboration with trusted professionals ensures an informed and successful hair restoration journey. If you’re considering taking the next step toward hair restoration, it’s crucial to have all your questions addressed by experts.
Book a Consultation today with our team at Hair Transplants Los Angeles and embark on your journey to confident, fuller hair. Your hair dreams are just a click away.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about FUE Hair Transplant Failures
Can an FUE Hair Transplant fail?
While FUE has a high success rate, there are instances where the transplant might not yield the desired results. Factors like surgeon expertise, post-op care, and patient health can influence outcomes.
What are the signs of an unsuccessful FUE transplant?
Signs can include unnatural hair growth patterns, excessive shedding post-transplant, prolonged redness, visible scarring, and lack of hair density in the transplanted areas.
How can I increase the chances of a successful FUE transplant?
Choose an experienced surgeon, follow post-op care instructions diligently, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and set realistic expectations.
How does FUE differ from other transplant methods?
FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles, making it minimally invasive with less visible scarring. In contrast, methods like FUT involve removing a strip of scalp, which can lead to more significant scarring.
Conclusion
Can FUE hair transplant fail… yes. FUE hair transplants can fail. However, it’s quite rare. In fact, with proper care and attention to detail, it is possible to have a successful procedure. It is essential to comprehend the potential dangers linked with FUE hair transplants before settling on a choice.
If you’re considering an FUE transplant, make sure that your doctor has experience performing these procedures. Be sure to follow their post-operative instructions carefully. With good aftercare and maintenance, you may find that an FUE hair transplant will give you the results that you desire without any of the potential complications or failures associated with them.
If you’re looking for a safe and effective solution to hair loss, consider FUE Hair Transplant. Our team of experienced professionals can help you determine if this procedure is right for your needs. With the right support before, during, and after your transplant procedure the “possibly” answer to “can FUE hair transplant fail” decreases significantly.
While there are no guarantees and everyone’s different. We stand by our work at Best Hair Transplant and hope you’ll contact us for a free consultation.
To ensure your ease of mind, you can view our customer recommendations HERE. Furthermore, you can also see our Google reviews and Yelp reviews. We can’t wait to help you start restoring your lost hair.